Imagine for a moment that your body’s immune cells are at a cocktail party, and antioxidants are the bouncers keeping the free radicals from starting trouble. You’ve likely heard the buzz about these molecular heroes and how they’re essential for your health, but you may not fully appreciate the complex dance they perform to keep your immune system in tip-top shape. As you navigate through the swarm of health advice and superfood trends, it’s vital to understand the real impact antioxidants have on your body’s defenses. They’re not just there to add a line on the nutrition facts of your favorite breakfast cereal; they play a pivotal role in managing oxidative stress and supporting your immune cells in the face of daily environmental challenges. Stick around, and you’ll uncover how these microscopic guardians contribute to your overall well-being and why your body relies on them to maintain a balanced immune response.
Key Takeaways
- Antioxidants, such as vitamin C, E, and A (beta-carotene), are crucial for maintaining cell integrity and optimal immune function.
- Vitamin C supplementation can reduce the severity and duration of upper respiratory infections.
- Antioxidant vitamins enhance tumor immunity activation and protect immune system components from environmental free radicals.
- Antioxidants, found in foods like citrus fruits, nuts, seeds, and carrots, play a central role in enhancing overall immune system function and warding off infections.
Understanding Antioxidants

Antioxidants are vital compounds that safeguard your cells by neutralizing the potentially harmful effects of free radicals produced through normal metabolic processes and environmental exposure. These substances play an indispensable role in maintaining the integrity of your body’s cells and are essential for the optimal functioning of the human immune system. As a component of your diet or as supplemental nutrition, antioxidants contribute significantly to your body’s overall antioxidant capacity, thus bolstering immune defenses.
Antioxidant vitamins, such as C, E, and A or beta-carotene, serve as cellular protectors. They stabilize free radicals that are either ingested or generated during the complex biochemical reactions within cells. By mitigating oxidative stress, these vitamins preserve cell structure and function, which is crucial for the immune system’s ability to respond effectively. In particular, vitamin C supplementation has been shown to reduce the severity and duration of upper respiratory infections, illustrating its impact on immune resilience.
Moreover, the antioxidant vitamins also protected the immune system’s components, enhancing tumor immunity activation and safeguarding against environmental free radicals that can compromise immune responses. The interaction between antioxidants and gut microbiota exemplifies the nuanced influence antioxidants have on immunity. By modulating gut flora, they reduce inflammation, a known instigator of immunological dysregulation, thereby supporting optimal immune function.
In essence, your body’s reliance on antioxidants is profound, with these substances underpinning the robustness of your immune responses. The administration of vitamins like A and C not only curtails infections but also reduces associated morbidity and mortality, as evidenced in vitamin A’s efficacy against measles. Consequently, antioxidants are paramount in the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases, representing a cornerstone in the maintenance of human health.
Antioxidants and Free Radicals
To effectively bolster your body’s defenses, it is crucial to understand how certain vitamins neutralize the cellular threats posed by free radicals. These potentially harmful molecules, called free radicals, can cause oxidative stress, which damages cells and compromises the immune system. Antioxidant vitamins such as C, E, and A, which include beta-carotene, play pivotal roles in enhancing immune function by neutralizing these radicals.
Antioxidant supplementation has been shown to improve certain immune responses. Clinical trials suggest that antioxidants can reduce severity and duration of respiratory infections, thereby supporting the immune system’s ability to combat pathogens. It’s important to note that these naturally occurring antioxidant compounds do more than just destroy free radicals; they also protect the structural integrity of cells and tissues, thereby preserving your body’s resilience against infections.
The following table illustrates the antioxidants, their sources, and their roles in immune health:
| Antioxidant | Sources | Role in Immune Health |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, bell peppers, strawberries | Enhances immune defense, protects against oxidative stress |
| Vitamin E | Nuts, seeds, spinach | Protects cell membranes from radical damage |
| Beta-Carotene | Carrots, sweet potatoes, kale | Supports mucosal immunity, neutralizes free radicals |
| Vitamin A | Liver, dairy products, fish | Maintains integrity of epithelial cells, immune enhancement |
Incorporating these antioxidants into your diet, whether through food sources or supplementation, can help destroy free radicals and reinforce your immune system. This proactive approach protects against environmental oxidative stressors and may significantly reduce the risk of illness. Remember, a strategic antioxidant regimen is a technical advantage in your quest to serve others by maintaining optimal health.
Immune System Enhancement
Understanding the role of antioxidant-rich foods and supplements in combating free radicals sets the stage for a broader discussion on how these nutrients can enhance the overall function of the immune system. As you delve into the intricacies of immune system enhancement, it’s crucial to recognize that antioxidants in the immune system play a pivotal role. Clinical evidence suggests that antioxidant supplementation, particularly with vitamins C, E, A, and beta-carotene, can significantly improve certain immune responses.
These antioxidants are not merely adjuncts; they are central to the immune system’s ability to ward off infections. For instance, vitamins C and E are known to protect the structural integrity of cells, including those cells involved in tumor immunity. This protective mechanism is particularly beneficial for the elderly, as it activates tumor immunity and safeguards immune responses against the deleterious effects of environmental free radicals.
Furthermore, the delicate balance between pro-oxidants and antioxidants within the immune system is preserved through nutrient targeting, which is essential for reducing inflammation and optimizing immune function. Antioxidant vitamins have been demonstrated to decrease morbidity and mortality by reducing the severity and duration of respiratory infections. This suggests a direct correlation between antioxidant supplementation and the immune system’s enhanced capability to combat pathogens.
To serve your community effectively, it’s imperative to understand that free radicals are associated with a plethora of health issues. By promoting the intake of antioxidants, you’re not only supporting the body’s natural defense mechanisms but also contributing to a more robust immune system that is better equipped to maintain health and wellbeing.
Antioxidants and Inflammation
Combatting inflammation, a key contributor to numerous diseases, requires a nuanced understanding of how specific antioxidants can modulate immune system responses. You must recognize that antioxidants serve as a defense mechanism against oxidative damage caused by free radicals, which are implicated in the inflammatory process. By neutralizing these unstable molecules, antioxidants help prevent the damage that can exacerbate inflammation.
Antioxidant supplementation, particularly with vitamins C and E, has been shown to enhance the cells involved in tumor immunity. This suggests that a targeted approach to antioxidant therapy could bolster the immune system’s capacity to combat neoplastic growths, while simultaneously mitigating the harmful effects of inflammation.
Furthermore, the protective role of antioxidant nutrients goes beyond the direct neutralization of free radicals; they also contribute to maintaining the delicate anti-/oxidative balance within the immune system. This balance is crucial for the immune system’s optimal function and its ability to ward off infections effectively.
The impact of environmental pollutants on immune response underscores the importance of antioxidants. These pollutants can induce oxidative stress, leading to inflammation and weakening immune defenses. By including antioxidants in your regimen, you’re providing an additional layer of protection against such environmental challenges.
In addition to their systemic benefits, antioxidants play a pivotal role in modulating gut microbiota. Given the gut’s significant influence on overall immune health, the ability of antioxidants to reduce inflammation in this area is particularly valuable.
Dietary Sources of Antioxidants
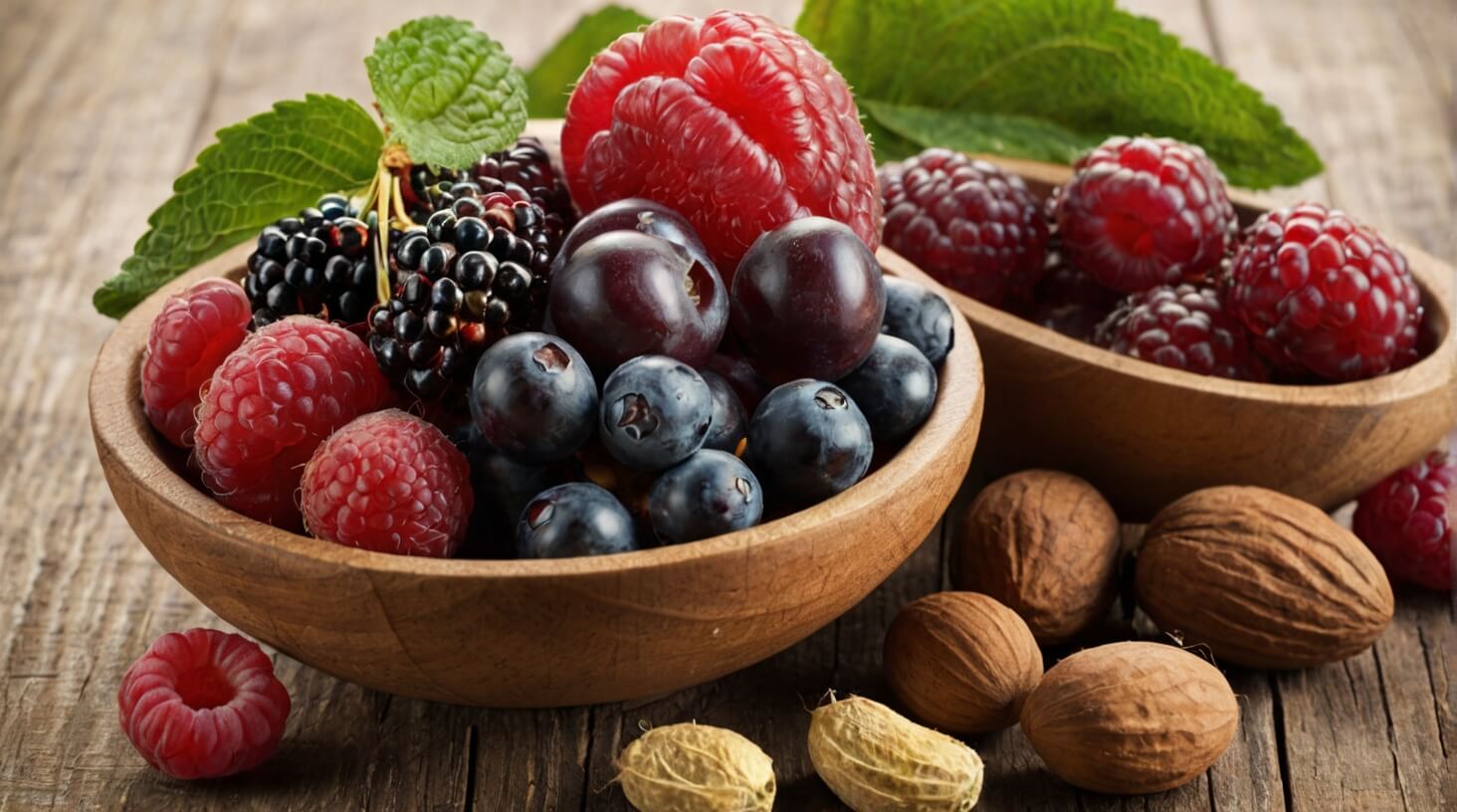

Incorporating a variety of fruits, such as berries, citrus fruits, and grapes, into your diet ensures a rich intake of antioxidants that support immune function. These foods contain naturally occurring antioxidants, including vitamin C and vitamin E, which are crucial in scavenging free radicals. Free radicals are by-products of normal cellular metabolism and external sources of free radicals such as pollution and UV light. Without adequate dietary antioxidants, these reactive molecules can lead to oxidative stress, potentially damaging cells and weakening immune responses.
Vegetables like spinach, kale, and sweet potatoes offer a substantial contribution to your antioxidant arsenal. They are not merely adjuncts but pivotal components in maintaining the equilibrium of redox processes within your body. These dietary antioxidants are instrumental in protecting the cells involved in tumor immunity and other critical aspects of the immune system.
Moreover, nuts and seeds, such as almonds and sunflower seeds, are potent sources of antioxidants. They deliver lipid-soluble antioxidants like vitamin E, which integrate into cell membranes, safeguarding them from oxidative damage. While antioxidant supplementation may be beneficial in certain contexts, obtaining antioxidants from whole foods ensures a balanced intake alongside other essential nutrients that synergistically enhance overall health.
Whole grains and herbs and spices also enhance your dietary antioxidant profile. Whole grains like brown rice and quinoa contribute complex antioxidants, while herbs and spices such as oregano, cinnamon, and turmeric are dense in these compounds. Integrating a diverse array of antioxidant-rich foods into your diet, rather than relying solely on supplements, is a holistic approach to fortifying your immune responses and supporting your body’s defense systems.