Imagine your body as a bustling city, where inflammation is the diligent police force keeping order, but when it becomes overzealous, it may inadvertently harm the very citizens it’s meant to protect. This is the delicate balance you must consider when exploring the connection between inflammation and cardiovascular health. While acute inflammation is a crucial response to injury or infection, it’s the chronic, low-grade inflammation that lingers like an unwelcome guest, contributing to the development of heart disease and other serious conditions. You’re likely aware that a healthy heart is central to overall well-being, but you may not realize how the persistent inflammation in your body can stealthily undermine this vital organ’s health. As you delve deeper into this discussion, you’ll uncover the nuanced ways in which inflammation can both safeguard and threaten your cardiovascular system, and why it’s essential to recognize the signs before they manifest into more significant issues.
Key Takeaways
- Inflammation plays a significant role in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases, particularly atherosclerosis.
- Chronic inflammation increases the risk of endothelial dysfunction, plaque buildup, and cardiovascular events.
- Elevated levels of inflammatory markers, such as cytokines and C-reactive protein, indicate higher cardiovascular risk.
- Targeting inflammation through lifestyle changes, anti-inflammatory diets, exercise, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits can help prevent and reduce the impact of cardiovascular diseases.
Understanding Inflammation’s Role
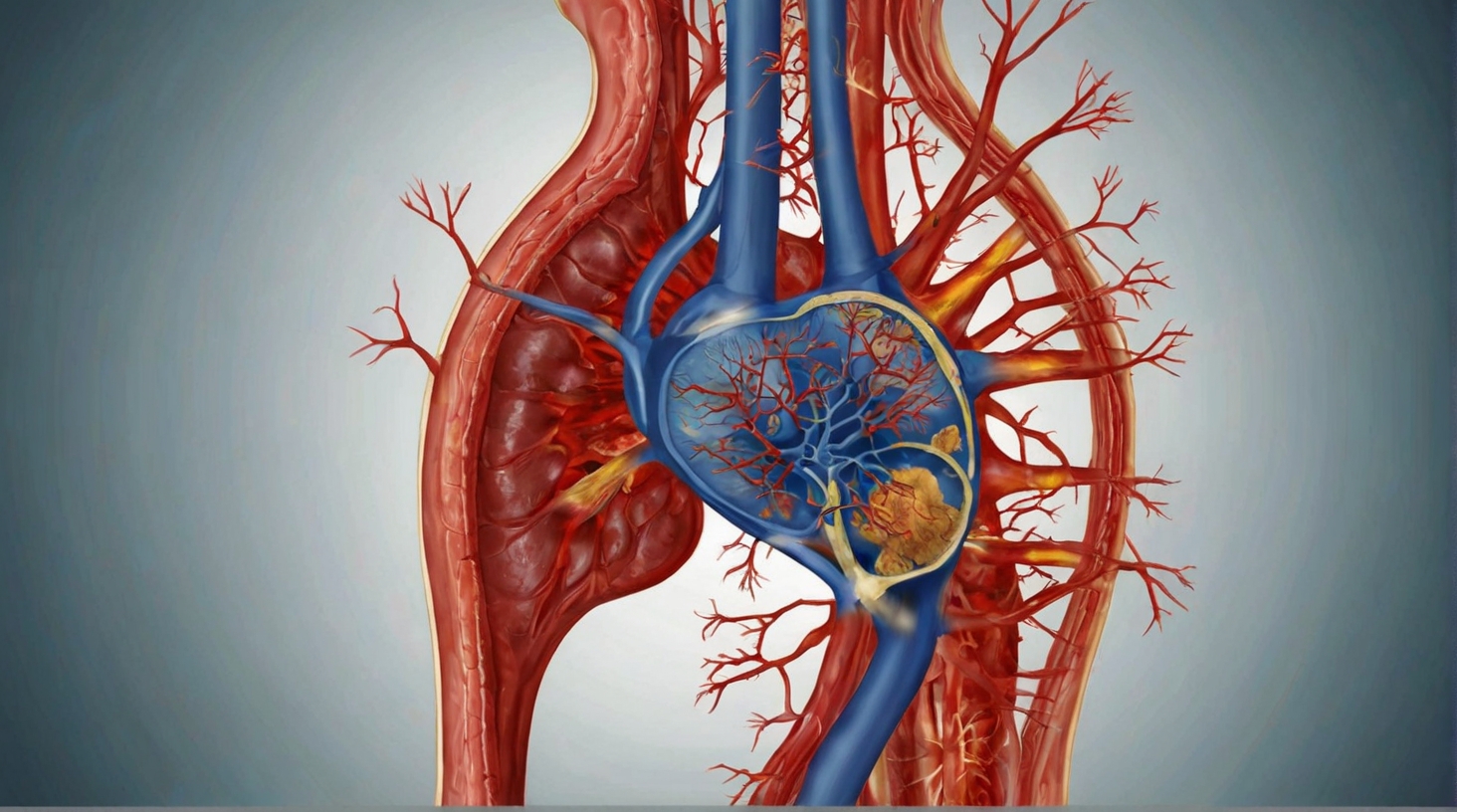
Inflammation acts as a catalyst in the early stages of atherosclerosis, thereby amplifying your risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. The process begins with endothelial dysfunction, where the inner lining of blood vessels becomes compromised. This dysfunction attracts immune cells to the site, instigating an inflammatory response. Over time, chronic inflammation exacerbates this condition, further injuring the endothelium and leading to the buildup of plaque.
Within the arterial walls, the sustained presence of inflammation disrupts the delicate balance required for cardiovascular health. The plaque formed in this environment is particularly unstable, predisposing you to a greater likelihood of heart attack. Inflammatory cytokines, which are markers of this insidious process, are crucial indicators of cardiovascular risk factors. Elevated levels of these cytokines, along with C-reactive protein, a substance produced by the liver in response to inflammation, are clear harbingers of potential cardiovascular events.
Moreover, chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, serve as a warning sign for increased cardiovascular risk. In these conditions, systemic inflammation correlates with a heightened threat to cardiovascular integrity.
The therapeutic targeting of inflammation has emerged as a promising avenue for reducing cardiovascular events. By mitigating the inflammatory cascade, the progression of atherosclerosis can be curtailed, thus diminishing the risk of adverse outcomes.
As someone committed to the well-being of others, understanding and addressing the inflammatory underpinnings of cardiovascular disease is essential. It enables you to identify at-risk individuals and intervene with strategies that target inflammation, potentially averting the development of life-threatening heart conditions.
Inflammation: The Heart Connection
Building on the understanding of inflammation’s pivotal role in cardiovascular disease, it’s crucial to examine how this response directly affects heart health. Inflammation plays a significant part in the progression of cardiovascular diseases, particularly in the formation of atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart attacks. Your immune system, while essential for healing, can sometimes become your heart’s adversary.
- Inflammation triggers the buildup of fatty deposits inside blood vessels, creating plaques that disrupt the smooth flow of blood.
- These plaques can rupture, causing a clot that blocks the flow of blood, potentially leading to a heart attack.
- Chronic inflammatory conditions are linked to higher risks of developing high blood pressure and subsequent cardiovascular events.
- Elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines in the blood are markers of increased cardiovascular risk and can predict worse outcomes during acute coronary syndromes.
The chronic inflammatory state associated with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus exemplifies the connection between systemic inflammation and heart health. The presence of persistent inflammation heightens the risk of heart-related complications. Similarly, periodontitis, an infection of the gums, has been linked with cardiovascular events, suggesting that inflammation in one part of the body can have far-reaching effects.
Recent advances in treating inflammation have shown promise in reducing the incidence of cardiovascular events. These findings underscore the importance of targeting inflammation to protect heart health. As someone dedicated to serving others, understanding and addressing the inflammatory processes can be vital in reducing the burden of cardiovascular diseases. By continuing to explore and apply immunomodulatory therapies, you can help to forge a path towards better cardiovascular outcomes for those at risk.
Chronic Inflammation’s Impact
Chronic inflammation significantly raises your risk of heart diseases, acting as a catalyst for a spectrum of cardiovascular complications. This persistent, low-grade inflammation is a critical factor in the development and progression of atherosclerosis, where cholesterol-rich plaques build up in your arteries. Elevated levels of C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation, are associated with a higher risk of developing heart issues, signaling the importance of understanding the role of inflammation in cardiovascular health.
| Cardiovascular Condition | Association with Chronic Inflammation |
|---|---|
| Coronary artery disease | Promotes plaque buildup and instability |
| Heart failure | Worsened by inflammatory cytokines |
| Aneurysms | Linked to inflammation’s progression |
| Acute coronary syndromes | Higher mortality with inflammation |
| Rheumatoid conditions | Elevated cardiovascular risk |
If you’re devoted to serving others, it’s vital to be aware of these associations and consider them as potential targets for treatments. Chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus are not only debilitating on their own but also elevate the risk of heart complications. Therapies targeting inflammatory pathways have shown promise in mitigating these risks and improving outcomes.
Informed by these facts, a precise approach to cardiovascular care must encompass strategies to reduce chronic inflammation. By doing so, you’re not just addressing the immediate inflammatory symptoms but also proactively combating the insidious threat to heart health. This analytical perspective empowers you to provide comprehensive care and potentially reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases in those you serve.
Anti-Inflammatory Strategies
To effectively combat the insidious threat of heart disease, adopting anti-inflammatory strategies in your lifestyle can be a transformative step towards better cardiovascular health. Inflammation plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of coronary heart disease and acute coronary syndrome. When plaque may rupture in your arteries, it can lead to myocardial infarction, often precipitated by high levels of C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation.
Consider these focused strategies to reduce the risk of inflammation-related cardiovascular events:
- Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet: Ingest foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Integrate Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activities that enhance blood flow and lower stress.
- Manage Stress Proactively: Implement practices like meditation and deep breathing.
- Prioritize Sleep Hygiene: Ensure you get quality sleep to support immune regulation.
By emphasizing these anti-inflammatory strategies, you’ll not only support the function of white blood cells in maintaining a healthy immune response but also promote overall vascular health. For instance, a diet abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can lower inflammation markers. Moreover, techniques to manage stress can reduce the burden on your cardiovascular system.
In some cases, medication might be necessary. The advent of targeted therapies like monoclonal antibodies designed to lower specific inflammatory substances in the blood has opened new avenues for treatment. However, the cornerstone of prevention remains in everyday choices that foster a less inflammatory state within your body.
In your quest to serve those at risk or suffering from heart disease, offer guidance that’s both practical and grounded in the latest research. Encourage the adoption of these anti-inflammatory habits as a fundamental part of a heart-protective lifestyle.
Future Research Directions
While you consider integrating these anti-inflammatory strategies into your daily regimen, it’s also essential to recognize the importance of ongoing research that aims to unravel the complex interactions between immune cells and cardiac function. Future research directions are pivotal in advancing our understanding of cardiovascular health, particularly in the context of inflammatory conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Exploring the impact of immune cells on cardiac cell function is not just an academic pursuit; it holds the potential to transform the management of heart disease. Delving into the inflammatory molecules—cytokines, for instance—secreted by immune cells, and dissecting their mechanisms within the cardiac cells, can lead to breakthroughs in how we approach conditions like acute coronary syndromes and high blood pressure.
Investigating the crosstalk between inflammation and cardiac cells is an analytical challenge that requires precision. Developing therapies that effectively disrupt this harmful dialogue could significantly improve outcomes for countless individuals grappling with heart issues. Moreover, the effectiveness of immunomodulatory therapies demands rigorous scrutiny to confirm their potential as viable therapeutic options.
Future research should particularly focus on targeting specific inflammation-related molecules, such as C-reactive protein, to develop novel therapeutic strategies. This approach could usher in a new era of personalized medicine where treatments are tailored to the unique inflammatory profile of an individual’s cardiovascular system.
Your role in this evolving landscape is critical. Staying informed and supportive of research efforts enables progress that could one day transform the prognosis for those with heart disease, turning today’s uncertainties into tomorrow’s solutions.