In the grand theater of your body, where the drama of various cells and tissues unfolds, inflammation stars as both hero and villain in the saga of your skin’s health. You’ve likely experienced the redness, heat, swelling, or pain accompanying an inflammatory response, signaling your immune system’s zealous attempts to protect you—sometimes a bit too overzealously. Particularly, in skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis, this fervent reaction can leave you with more than just an itch to scratch. As you navigate the tightrope between necessary defense and chronic discomfort, you’ll find that understanding the delicate balance of your body’s inflammatory processes is essential. Stick around to uncover the intricate dance of cells and signals that can turn the tide from persistent irritation to relief and how you might orchestrate a more harmonious interaction between your immune system and your skin.
Key Takeaways
- Inflammation is an immune response that occurs when the skin barrier is breached.
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions result from dysregulated immune responses.
- Infections can exacerbate inflammatory skin conditions.
- Immune system dysfunction can lead to dermatological disorders.
Understanding Inflammation
While your skin often acts as a barrier to protect your body, inflammation can arise as an immune response when this barrier is breached by injury or infection. This response is orchestrated by a complex interplay of immune cells releasing inflammatory cytokines, signaling molecules that escalate the reaction. These cytokines include interleukins, tumor necrosis factors, and chemokines which together coordinate the inflammatory response.
In the case of chronic inflammatory skin conditions, such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, and psoriasis, the immune response becomes dysregulated. This results in persistent inflammation, leading to symptoms like redness, swelling, and pain. In atopic dermatitis, for example, an overactive immune response to environmental or internal triggers causes skin irritation and barrier dysfunction. Contact dermatitis follows a similar pattern but is typically triggered by direct contact with allergens or irritants.
Psoriasis, on the other hand, involves the rapid proliferation of keratinocytes, the predominant cell type in the outer layer of the skin. This hyper-proliferation, combined with inflammation, leads to the thick, scaly plaques characteristic of the disease. The inflammation in psoriasis is driven in part by T cells, a type of white blood cell that is central to the immune response.
Furthermore, autoimmune diseases can precipitate chronic inflammatory skin reactions, with the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy skin cells. Understanding these mechanisms is critical for tailoring interventions and mitigating the debilitating effects of these conditions.
To this end, targeting inflammasomes, protein complexes crucial to the immune response, has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy. By modulating these complexes, healthcare professionals might better manage the inflammatory processes underlying various skin diseases.
Common Inflammatory Skin Conditions
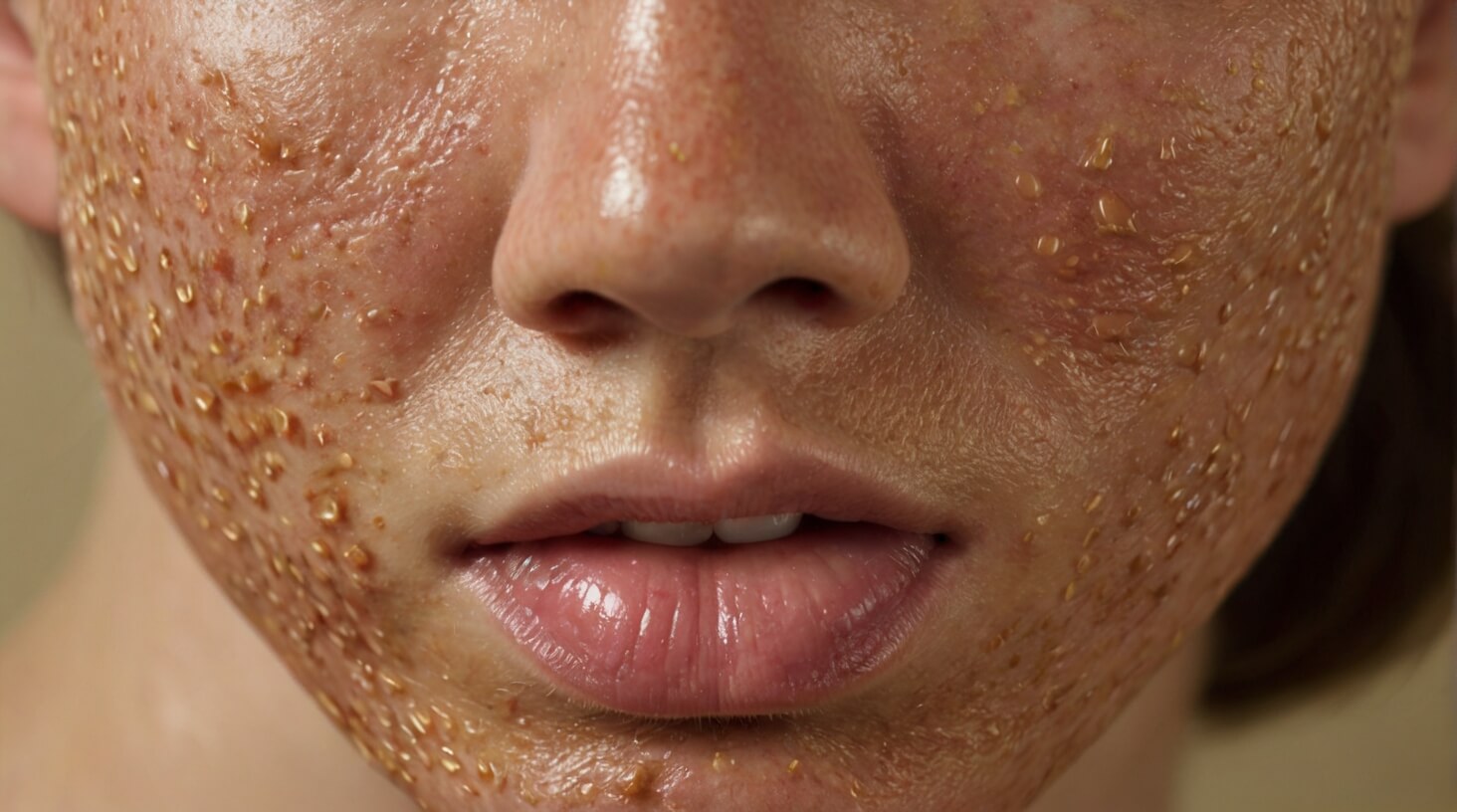
Eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and psoriasis are common inflammatory skin conditions that manifest through symptoms such as flaking, itching, and discomfort, necessitating a nuanced understanding of their etiology and management. These dermatological challenges often require partnering with a dermatologist to tailor an effective treatment strategy.
Eczema is characterized by an immune reaction that leads to inflamed, itchy, and sometimes oozing skin lesions. Contact hypersensitivity also plays a role, where certain allergens trigger eczematous flare-ups. Management includes avoiding irritants and using moisturizers and topical steroids to control symptoms.
Seborrheic dermatitis, primarily affecting the scalp and face, involves an inflammatory response to Malassezia yeasts. This results in flaky, red skin. Antifungal treatments and anti-inflammatory agents are typically employed to alleviate this condition.
Psoriasis, with varied forms such as plaque psoriasis and guttate psoriasis, is marked by hyperproliferation of keratinocytes and an influx of immune cells, leading to raised, red patches covered with white scales. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and mast cells are central to the pathophysiology of psoriasis. Systemic and topical therapies are used to moderate the immune response and soothe skin.
Lupus erythematosus, though less common, is another inflammatory skin disease with potential systemic implications. It presents with a range of cutaneous manifestations, from malar rashes to discoid lesions, and requires a comprehensive approach to management.
These conditions not only cause physical symptoms but may also contribute to emotional distress. Effective management strategies are integral in mitigating the impact on quality of life, underscoring the importance of a compassionate approach to care for individuals with inflammatory skin diseases.
Infection-Induced Inflammation
Infections can exacerbate inflammatory skin conditions by intensifying symptoms and prolonging flare-ups, necessitating a dual-focused treatment strategy to manage both the underlying infection and the cutaneous manifestations. When you’re faced with infection-induced inflammation, it’s not just the pathogens at play—your body’s immune cells are also key actors in this drama. They rush to the site of infection, unleashing a cascade of inflammatory responses that, while meant to protect, can also cause skin inflammation and exacerbate symptoms of skin conditions.
Understanding how the immune response in the skin goes awry is crucial, especially when the pathogenesis of psoriasis or other skin conditions is influenced by such infections. The battle between pathogens and immune responses can trigger allergic reactions, leading to a vicious cycle of inflammation and skin damage.
To alleviate these challenges, consider the following:
- Prompt Identification: Recognize early signs of infection to prevent complications.
- Comprehensive Approach: Employ treatments targeting both the infection and inflammation, ensuring the best treatment outcomes.
- Continual Education: Stay informed about the causes of skin inflammation to enhance your ability to serve patients effectively.
Infection-induced inflammation is a complex interplay that can significantly impact the well-being of those with chronic skin conditions. Tailoring the best treatment plans requires a deep dive into the specifics of each case, including the type of infection and the individual’s unique skin pathology. With a compassionate and educated approach, you can help mitigate the distress caused by these conditions and guide patients towards healthier, more comfortable skin.
Immune System Dysfunction

Immune system dysfunction, characterized by either hyperactivity or insufficient response, can precipitate a spectrum of dermatological disorders, including chronic inflammation and tissue damage. When your immune system is compromised, it fails to protect the skin effectively, often leading to an inflammatory state. This dysfunction can cause painful symptoms and may increase the risk of developing severe skin conditions.
A hyperactive immune response may result in conditions like psoriasis, where immune cells attack healthy skin tissue, or eczema, which involves an allergic response leading to itchy, inflamed skin. Conversely, an underactive immune system might not ward off pathogens, causing vulnerability to infections that can exacerbate skin issues.
Treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the immune dysfunction. Here’s a table that outlines common causes, the resulting skin reaction, and potential treatments:
| Common Causes | Skin Reaction | Potential Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Autoimmune disorders | Chronic inflammation | Immunosuppressants |
| Allergies | Allergic dermatitis | Antihistamines, corticosteroids |
| Genetic predispositions | Eczema, psoriasis | Targeted biologic therapies |
| Environmental factors | Acne, rashes | Avoidance of triggers, topical treatments |
Understanding the immune system’s role in skin health is vital. You’re in a position to provide relief and support to those affected by these conditions. It’s essential to recognize the signs of immune dysfunction and address them promptly with appropriate, evidence-based interventions. As you serve others, your knowledge can be instrumental in managing inflammation and improving their quality of life.
Lifestyle Factors and Skin Health

Your lifestyle choices, including diet, activity levels, and substance use, can significantly impact the prevalence and severity of inflammatory skin conditions. For instance, individuals with obesity are at a higher risk for diseases such as psoriasis due to increased inflammation in the skin. Similarly, habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to a greater incidence of psoriasis and may exacerbate its pathology.
To maintain optimal skin health, consider these lifestyle modifications:
- Dietary Adjustments: A balanced diet, potentially including gluten-free options for those with celiac disease, can mitigate inflammatory responses and support the treatment of psoriasis.
- Regular Exercise: Adequate physical activity helps reduce body weight and systemic inflammation, potentially decreasing the occurrence of common skin issues like dry skin and heat rash.
- Substance Moderation: Limiting or abstaining from smoking and alcohol intake can reduce the severity of skin conditions and promote overall dermal health.
Sleep disturbances are also a notable risk factor for inflammatory skin diseases, emphasizing the importance of restorative sleep in skin health. Moreover, the work environment and lifestyle can contribute to inflammation, potentially triggering an allergic response or exacerbating existing conditions.
In severe cases, these lifestyle factors may not only influence the onset of skin disorders but also affect the efficacy of treatments. Therefore, addressing these factors holistically is crucial for both preventing and managing inflammatory skin conditions effectively. As you serve others, understanding and communicating the significance of lifestyle factors in skin health becomes an essential component of comprehensive care.
Effective Inflammatory Skin Treatments
Selecting the right treatment for inflammatory skin conditions like eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, and psoriasis is crucial to alleviate symptoms such as flaking and itching effectively. The cornerstone of managing these conditions lies in identifying and mitigating potential causes, which may involve an allergic response or other triggers. A comprehensive skin test, often conducted by a dermatologist, can pinpoint such triggers, enabling tailored interventions.
When you’re dealing with inflamed skin, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the most effective inflammatory skin treatments. Below is a table summarizing potential treatment options:
| Condition | Treatment | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Eczema | Hydrocortisone cream | Reduces inflammation and itching |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Antifungal creams | Targets yeast that can worsen inflammation |
| Psoriasis | Topical retinoids | Regulates skin cell growth and reduces scaling |
In addition to pharmacological treatments, non-pharmacological strategies such as stress management and skincare routines are essential. Harvard Medical School Guides provide compact, authoritative information that can further educate on these topics. Your role in serving others includes guiding them toward these resources and helping them understand their skin symptoms and conditions.
Home Remedies for Relief
Several home remedies offer symptomatic relief for inflammatory skin conditions, utilizing natural ingredients with proven anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. When you’re dealing with skin inflammation, understanding the causes and identifying symptoms—including redness, itching, and swelling—is crucial in selecting the most effective home remedies.
Here are three home remedies you can recommend to those seeking relief from inflammatory skin symptoms:
- Oatmeal Baths: A classic solution for soothing irritated skin, oatmeal contains compounds known as avenanthramides that reduce inflammation.
- Aloe Vera Gel: This gel, extracted from the leaves of the aloe plant, is renowned for its cooling and healing properties, making it ideal for treating allergic skin reactions.
- Tea Tree Oil: With potent antibacterial and anti-inflammatory qualities, diluted tea tree oil can aid in calming skin flare-ups.
These remedies can serve as adjuncts to medical treatments, addressing the common symptom of discomfort associated with skin conditions. It’s important to note that while allergic responses may be alleviated with topical applications, systemic causes of skin symptoms require comprehensive intervention.
Beyond topical treatments, dietary modifications can also play a role in managing skin inflammation. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, and antioxidants supports the body’s natural anti-inflammatory response.